
Diagnostic Kits
Diagnostic Kits
- Cannabis Gender ID Kit
- HLVd Cannabis qPCR Kit
- Plant Pathogen Detection Kit
- Animal Pathogen Detection Kit
Back
Reagents
Clinical Chemistry
CRISPR
Immunodiagnostics
Molecular Diagnostics
Next-Generation Sequencing
In Vitro Transcription
General IVD Reagents
Glycerol-Free Enzymes
Back
Services
Support
About
Cart



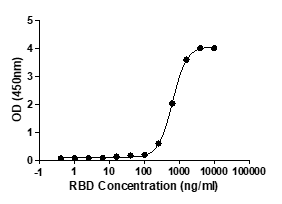

 2019-nCoV Spike protein RBD (L452R, E484Q), HRP conjugated , C19SD-G231DD
2019-nCoV Spike protein RBD (L452R, E484Q), HRP conjugated , C19SD-G231DD